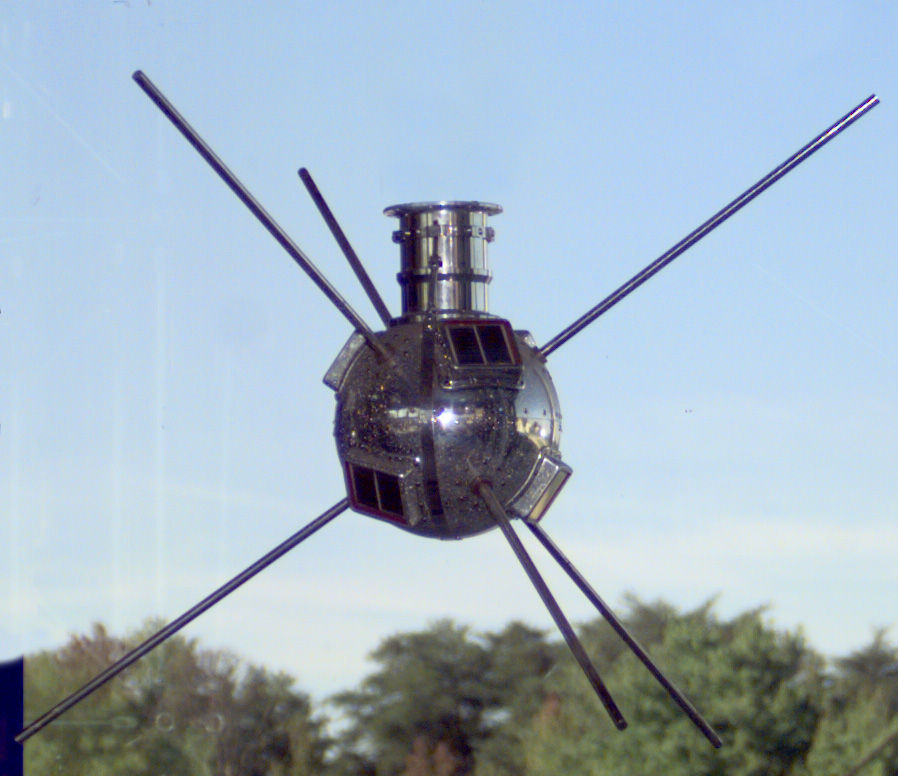
Twenty-five years ago today — March 25, 1988 — a joint U.S.-Italy mission lifted off from the San Marco Range, Kenya, on a Scout launch vehicle.

(Scout X-4 rocket with the earlier US-Italian satellite San Marco 1. NASA image from Wikimedia Commons.)
The last satellite orbited from the San Marco facility on the Kenyan coast, San Marco D/L carried a specialized suite of sensors to study the interaction between the solar wind and the Earth’s thermosphere and ionosphere. One instrument, the Wind and Temperature Spectrometer, failed after 20 days, but the rest of the spacecraft operated nominally. Though the satellite was intended to last a full year, it re-entered the atmosphere on December 6, 1988.