Twenty-five years ago today — October 5, 1984 — space shuttle mission STS-41G launched from the Kennedy Space Center.

(STS-41G mission patch. NASA image. Click to enlarge.)
Space Shuttle Challenger carried U.S. astronauts Robert L. Crippen, Jon A. McBride, Kathryn D. Sullivan, Sally K. Ride, David C. Leestma, and Paul D. Scully-Power, and Canadian astronaut Marc Garneau. This was the first space flight to include two women, and Kathryn Sullivan became the first female U.S. astronaut to perform a spacewalk. Garneau was the first Canadian payload specialist to fly in space, and Scully-Power was the first oceanographer in space.
The crew deployed the Earth Radiation Budget Satellite early in the flight; the ERBS was part of a larger Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE) comparing the energy absorbed by the earth with what the planet emits into space.
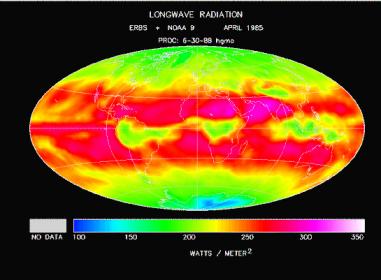
(ERBE longwave radiation data. NASA image.)
The crew spent the rest of their eight days in orbit performing various experiments. In one, they demonstrated the possibility of refueling satellites in orbit.